C#, Windows Forms Tips and Tricks
Convert System.Data.SqlTypes.SqlMoney and round it to CHF 0.5
System.Data.SqlTypes.SqlMoney monLohnsumme;
while (this._sqlReader.Read())
{
strNachName = _sqlReader.GetString(4);
strValue = Convert.ToString(_sqlReader.GetDateTime(8).Month);
monLohnsumme = _sqlReader.GetSqlMoney(10);
ConvertMoney(monLohnsumme)
}
private string ConvertMoney(System.Data.SqlTypes.SqlMoney pMoney)
{
double dMoney = ConvertMoney(pMoney.ToDouble());
return dMoney.ToString();
}
// Round Money
private double ConvertMoney(double pMoney)
{
return System.Math.Round(pMoney*20)/20;
}
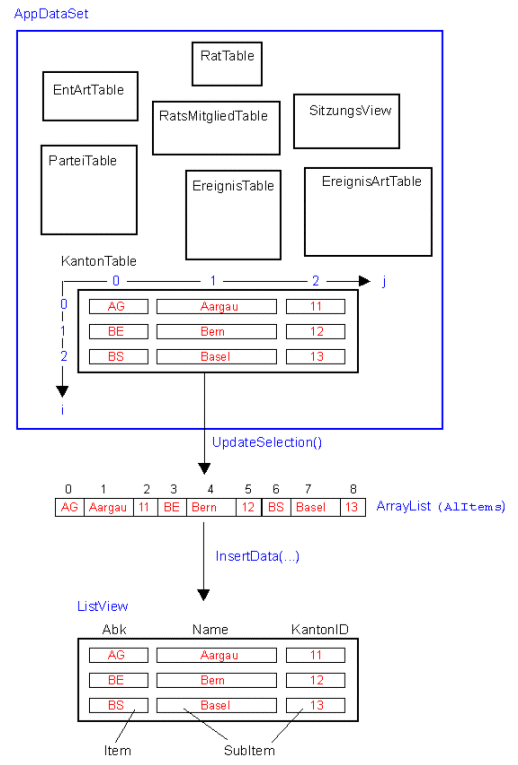
How to dynamically fill a ListView from a DataSet Table
// Fill ArrayList with Data from DataSet Table
drcRows = AppDataSet.GetInstance().KantonTable.Rows;
arrColumns = new string[]{"Abk","Name","KantonID"};
arrColumnHeader = new string[]{"Abk","Name","ID"};
arrColumnWidth = new int[]{80,436,0};
for (int i=0; drcRows != null && i<drcRows.Count; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<arrColumns.Length; j++)
{
alItems.Add((object)drcRows[i][arrColumns[j]]);
}
}ListViewColumnSorter.DataType[] lvcs = { ListViewColumnSorter.DataType.text, ListViewColumnSorter.DataType.text }; columnTypes = lvcs;InsertData(alItems, arrColumnHeader, arrColumnWidth, columnTypes);
// Fill ListView with Data from ArrayList
public void InsertData(ArrayList pAlItems, string[] pColumns, int[] pColumnWidth,
ListViewColumnSorter.DataType[] pColumnTypes)
{
int width;
iNumColumns = pColumns.Length;
// Add Column Headers to the ListView
lvGeneric.Columns.Clear();
for (int i=0; i<iNumColumns-1; i++)
{
width = (lvGeneric.Width - 30/*scrollbar*/) / (iNumColumns - 1);
if (pColumnWidth != null && pColumnWidth.Length > i)
{
width = pColumnWidth[i];
}
lvGeneric.Columns.Add((string)pColumns[i], width,
HorizontalAlignment.Left);
}
// Add Rows to the ListView
lvGeneric.Items.Clear();
for (int i=0; i<pAlItems.Count; i+=iNumColumns)
{
ListViewItem lvi = new ListViewItem(pAlItems[i].ToString());
for (int j=1; j<iNumColumns; j++)
{
lvi.SubItems.Add(pAlItems[i+j].ToString());
}
lvGeneric.Items.Add(lvi);
}
if (pColumnTypes != null)
{
lvGeneric.SortColumn = pColumnTypes;
}
}
ReadOnly Columns
Gets or sets a value indicating whether the column allows changes once a row has been added to the table.
If a column is read-only it is still changeable in GUI but does not pass a value to the database. However, if we list it inside a SQL-INSERT or UPDATE statement we need the control's value. Typically all columns that are selected with functions (e.g. CONVERT) are set automatically to read-only.
public virtual void FillSchema(DataSet pDataSet) { try { _sqlda.FillSchema(pDataSet, SchemaType.Mapped, _strTableName); DataTable dtable = pDataSet.Tables[_strTableName]; foreach (DataColumn dcol in dtable.Columns) { dcol.ReadOnly = false; } } catch (SqlException ex) { throw new AkException(8, ex); } }
Working with Null Data Fields
Here are a few tips to help you correctly use null field values in the .NET Data Architecture
Always set the value of a null field using the System.DBNull class.
Always use the IsNull method of the DataRow class to test for null values from a database. This method is the only supported way to test for null database values.
// In all columns of all modified rows of a table, this method replaces
// empty strings with DBNull
private void ReplaceEmptyStringWithDBNull(DataTable pTable)
{
foreach (DataRow drow in pTable.Rows)
{
// Do nothing if this row is deleted
if (drow.RowState == DataRowState.Deleted)
{
continue;
}
// Replace empty strings
foreach (DataColumn dcol in pTable.Columns)
{
if (drow[dcol].ToString() != null)
{
if (drow[dcol].ToString().Trim() == String.Empty)
{
drow.BeginEdit();
drow[dcol] = System.DBNull.Value;
}
}
}
}
}If it is possible that a data field contains a null value, be sure to test for it (with the IsNull method) before using the value in a context that expects a non-null value. A typical example of this is Integer-valued data fields that may be null. Note that the .NET run time Integer datatype does not include the null value.
Here is an example
int i = rowStudent["ZipCode"]; // Throws exception if null!