How to create a read-only Replication
Overview
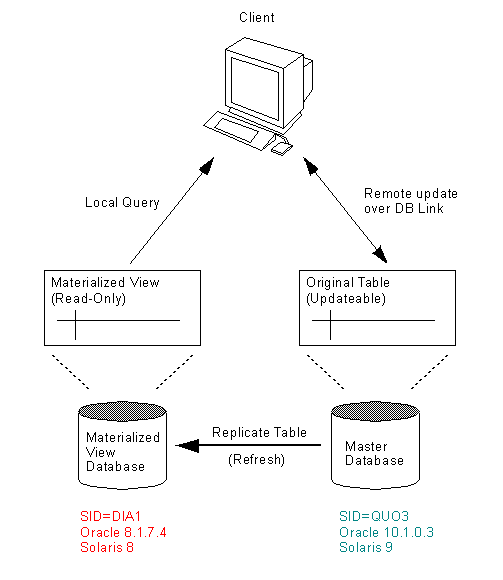
Read-only snapshot sites can be used to provide local access to remote master tables. Having a local snapshots of the data improves query response time. Updates can only be issued against the master table.
Starting from Oracle10g Read-only Snapshots are so called Read-Only Materialized Views
Read-Only Materialized Views
In a basic configuration, materialized views can provide read-only access to the table data that originates from a master site or master materialized view site. Applications can query data from read-only materialized views to avoid network access to the master site, regardless of network availability. However, applications throughout the system must access data at the master site to perform data manipulation language changes (DML). The master tables and master materialized views of read-only materialized views do not need to belong to a replication group.
Read-only materialized views provide the following benefits:
Eliminate the possibility of conflicts because they cannot be updated.
Support complex materialized views. Examples of complex materialized views are materialized views that contain set operations or a CONNECT BY clause.
Example
In order to create one (or many) read-only snapshot of the master Oracle database tables, the following steps are necessary.
Master Site: Oracle 10.1.0.3, Solaris 9, SID=QUO3
Snapshot Site: Oracle 8.1.7.4, Solaris 8, SID=DIA1
Check TNSNAMES.ORA
- On Master (Host=quorum)
DIA1.WORLD =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = diamond)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = DIA1)
(INSTANCE_NAME = DIA1)
(SRVR = DEDICATED)
)
)
DIA1 =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = diamond)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = DIA1)
(INSTANCE_NAME = DIA1)
(SRVR = DEDICATED)
)
)On Snapshot (Host=diamond)
QUO3.WORLD =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = quorum)(PORT = 1523))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = QUO3)
(INSTANCE_NAME = QUO3)
(SRVR = DEDICATED)
)
)
QUO3 =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = quorum)(PORT = 1523))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = QUO3)
(INSTANCE_NAME = QUO3)
(SRVR = DEDICATED)
)
)
Create DB Links
On Master (Host=quorum)
sqlplus scott/tiger@QUO3
CREATE DATABASE LINK DIA1 CONNECT TO scott IDENTIFIED BY tiger using 'DIA1';
Database link created.On Snapshot (Host=diamond)
sqlplus scott/tiger@DIA1
CREATE DATABASE LINK QUO3 CONNECT TO scott IDENTIFIED BY tiger using 'QUO3';
Database link created.desc emp@QUO3;
Name Null? Type
----------------------------------------- -------- ----------------------
EMPNO NOT NULL NUMBER(4)
ENAME VARCHAR2(10)
JOB VARCHAR2(9)
MGR NUMBER(4)
HIREDATE DATE
SAL NUMBER(7,2)
COMM NUMBER(7,2)
DEPTNO NUMBER(2)
Create Snapshot Log
For each table, which should be replicated, a SNAPSHOT LOG must be created (as user, who owns the table).
A materialized view log (Snapshot Log) is a table at the materialized view's master site or master materialized view site that records all of the DML changes to the master table or master materialized view. A materialized view log is associated with a single master table or master materialized view, and each of those has only one materialized view log, regardless of how many materialized views refresh from the master. A fast refresh of a materialized view is possible only if the materialized view's master has a materialized view log. When a materialized view is fast refreshed, entries in the materialized view's associated materialized view log that have appeared since the materialized view was last refreshed are applied to the materialized view.
On Master (Host=quorum)
sqlplus scott/tiger@QUO3
DROP SNAPSHOT LOG ON emp;
CREATE SNAPSHOT LOG ON emp
TABLESPACE tab
STORAGE
(INITIAL 200K
NEXT 200K
MINEXTENTS 1
MAXEXTENTS UNLIMITED
PCTINCREASE 0);
Materialized view log created.
Create Snapshot
A snapshot contains on the remote site the data of the master table. All data changes are reflected in the snapshot after a refresh of the snapshot (either triggered manually or automatically).
On Snapshot (Host=diamond)
sqlplus scott/tiger@DIA1
CREATE SNAPSHOT emp
PCTFREE 15
STORAGE
(INITIAL 200K
NEXT 200K
PCTINCREASE 0)
TABLESPACE tab
USING INDEX
PCTFREE 0
STORAGE
(INITIAL 200K
NEXT 200K
PCTINCREASE 0)
TABLESPACE idx
REFRESH FORCE
START WITH SYSDATE NEXT SYSDATE+(1/1440) /* 60 SECONDS */
AS SELECT * FROM emp@QUO3;
Materialized view created.
Create Synonym
On Snapshot (Host=diamond)
sqlplus scott/tiger@DIA1
CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM emp FOR scott.emp;
Synonym created.Now, you can access the table emp locally which will be automatically refreshed every 60 sec.
Refresh the Snapshot
The snapshot on the remote site must be refreshed regularily. This can be done bullet either by hand after a substantial change on the master site or in regular intervalls.
Manual Refresh
On Snapshot (Host=diamond)
sqlplus scott/tiger@DIA1
execute dbms_snapshot.refresh('scott.emp','F');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.The first parameter is a list of snapshots to be refreshed. The second describes the method, F stands for FAST refresh (only changes in the master table are propagated, C stands for complete refresh.
There is also a dbms_snapshot.refresh_all routine. It requires some more privileges.
execute dbms_snapshot.refresh_all;
Automatic Refresh
Automatic refresh is realized by parameters for a refresh group or by the definition of the snapshot. In order to run periodoc jobs in the database (as automatic refresh jobs), the ability to run SNP background jobs must be given.
Especially, in the file init<instance>.ora , located the parameterjob_queue_processes = 1
must be included (the default is 0) and the database must be restarted! This parameter allows background processes to be executed in one job queue.
Check Automatic Refresh
You may use the following query to check, if automatically refresh works.
SELECT SUBSTR(job,1,4) "Job", SUBSTR(log_user,1,5) "User",
SUBSTR(schema_user,1,5) "Schema",
SUBSTR(TO_CHAR(last_date,'DD.MM.YYYY HH24:MI'),1,16) "Last Date",
SUBSTR(TO_CHAR(next_date,'DD.MM.YYYY HH24:MI'),1,16) "Next Date",
SUBSTR(broken,1,2) "B", SUBSTR(failures,1,6) "Failed",
SUBSTR(what,1,20) "Command"
FROM dba_jobs;
Job User Schem Last Date Next Date B Failed Command
---- ----- ----- ---------------- ---------------- - ------ --------------------
2 SCOTT SCOTT 06.09.2005 15:05 06.09.2005 15:06 N 0 dbms_refresh.refresh
Drop Snapshots and Snapshot Logs
On Master (Host=quorum)
sqlplus scott/tiger@QUO3
spool drop_snapshot_logs.sql
select 'PROMPT Dropping Snapshot Log for '||MASTER||chr(10)
||'drop snapshot log on '||MASTER||';'
from USER_SNAPSHOT_LOGS;
spool off
@drop_snapshot_logs.sql
PROMPT Snapshot Logs DroppedOn Snapshot (Host=diamond)
sqlplus scott/tiger@DIA1
spool drop_snapshots.sql
select 'PROMPT Dropping Snapshot for '||NAME||chr(10)
||'drop snapshot '||NAME||';'
from USER_SNAPSHOTS;
@drop_snapshots.sql
PROMPT Snapshots dropped
Refresh Groups
If the snapshot must obey certain integrity rules, like referential integrity, then the refresh of the snapshot tables must be synchronized. This is achieved by creating refresh groups.
dbms_refresh.make(
name => 'MY_GRP',
list => 'emp,dept,bonus,salgrade',
next_date => SYSDATE,
interval => 'SYSDATE + (1/1440)', /* 60 seconds */
implicit_destroy => TRUE, /* delete the group if substracting
the last member */
lax => TRUE, /* delete from other group if already
existing in a group */
rollback_seg => 'RB06'
);
commit;