T-SQL Debugging with the SQL 2000 Desktop Engine
Overview
Visual Studio .NET offers a direct debugging interface to T-SQL procedures and functions. There are two ways for SQL Debugging, local and remote.
Local T-SQL Debugging with the SQL 2000 Desktop Engine
Local debugging can be accomplished more easily than many people realize. A full installation of Visual Studio .NET installs MSDE 2000, which is the SQL Server database engine without a license for client tools such as the Enterprise Manager or Query Analyzer. By connecting to your remote database using the SQL Enterprise Manager, you can script your remote database to a file. Run the script on your local MSDE 2000 database, load sufficient data for testing, and then debug your stored procedures locally.
Perform the following Steps
Install SQL 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE) as described here.
SQL Server can run under the System Account:
We installed MSDE under D:\MSDE
Install Enteprise Manager and Query Analyzer from the SQL Server CD
We installed this Client Tools under: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\80
Install Visual Studio 2003 with SQL Debugging
This should install the DLL for the SQL Debugging mssdi98.dll to the
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\80\Tools\Binn Directory
The Version with 184'320 Bytes is the correct DLL.
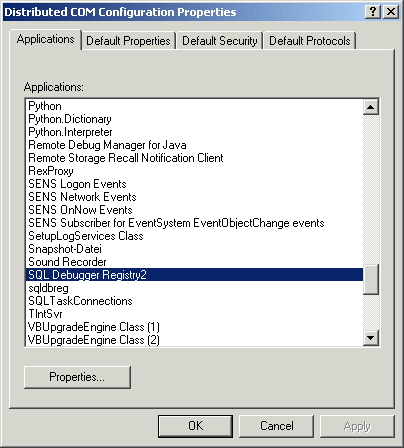
Check the DCOM Entry
Run dcomcnfg.exe from the CMD Shell, check that SQL Debugger Registry2 is under «Applications».
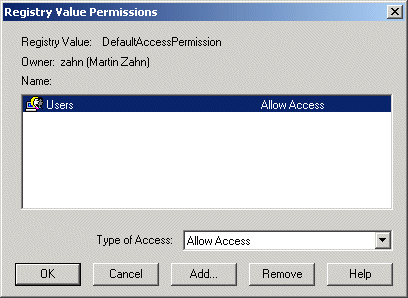
Set the Access Rights under «Default Security».
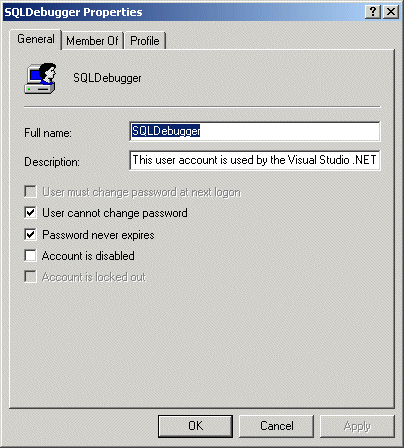
Check the «SQLDebugger» User Account.
- Grant execute permission on the stored procedure, sp_sdidebug, to the debugger user by executing the following command in Query Analyzer:
USE master
GRANT EXECUTE
ON sp_sdidebug
TO public
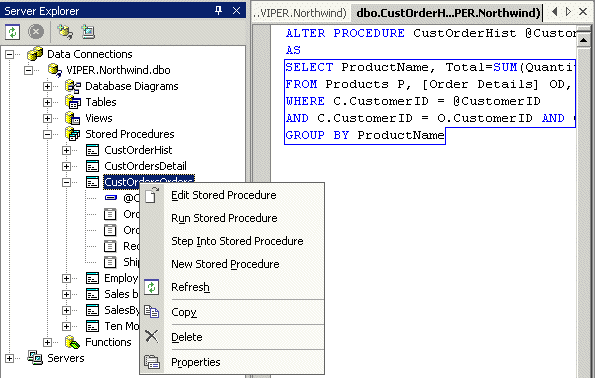
Ready - Debug your Stored Procedure from within Visual Studio 2003
Visual Studio .NET’s T-SQL Debugger is a full featured tool. You can set breakpoints and change the values of variables as you debug much the same as you would when debugging other languages.